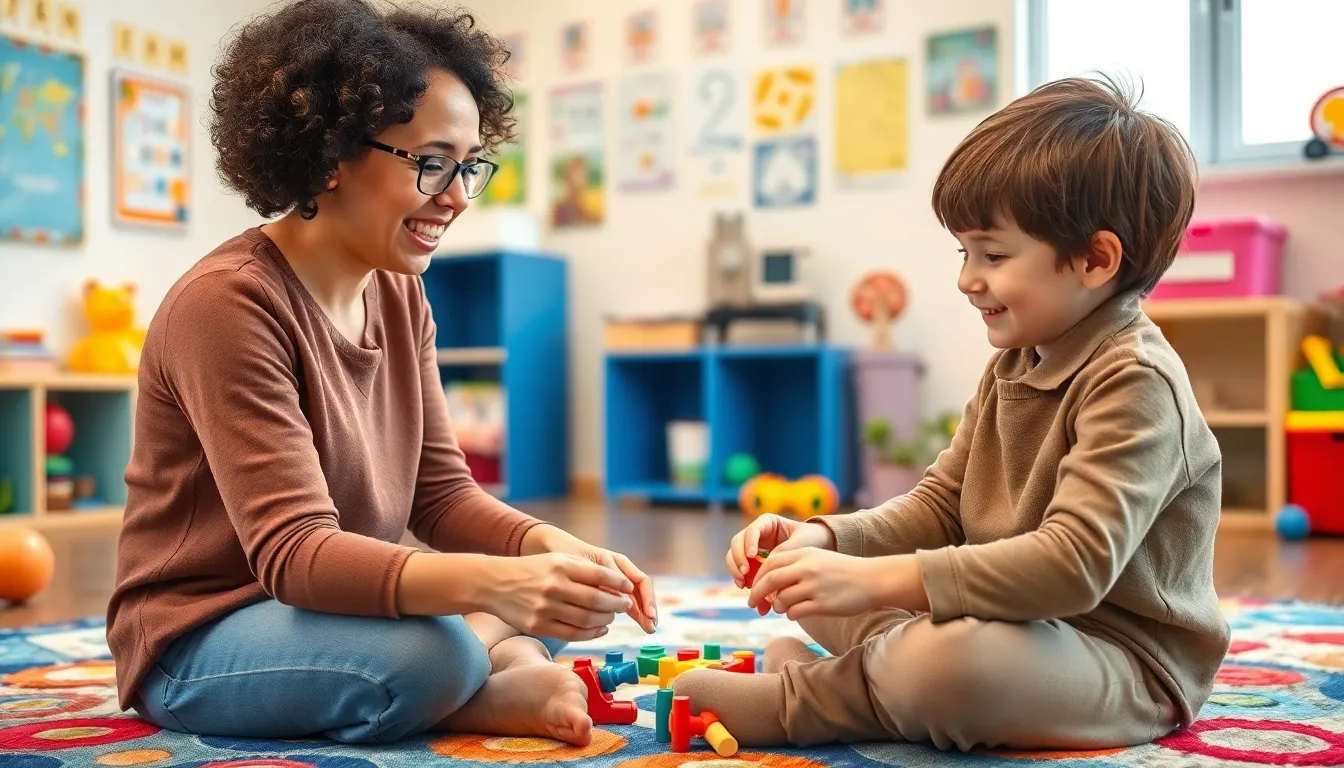
Behavioral therapy for children is a powerful tool that addresses various emotional and behavioral challenges. As kids navigate the complexities of growing up, they may face difficulties like anxiety, ADHD, or social skills deficits. This therapeutic approach focuses on modifying harmful behaviors and fostering positive ones through structured interventions.
Parents and caregivers often seek effective solutions to help their children thrive. Behavioral therapy not only equips children with essential coping strategies but also enhances their overall emotional well-being. By understanding the principles behind this therapy, families can make informed decisions and support their child’s development in a nurturing environment.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Behavioral Therapy for Children
Behavioral therapy for children addresses emotional and behavioral challenges, offering structured interventions that foster positive behavior changes. This therapeutic approach effectively targets issues such as anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and social skills deficits, allowing children to develop coping strategies and enhance emotional well-being.
Therapists implement techniques like positive reinforcement, where desired behaviors receive rewards, and negative reinforcement, where undesired behaviors lose privileges. Such methods modify behavior through consistent feedback and structured environments. Techniques may include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – This evidence-based practice teaches children to identify and challenge negative thought patterns, promoting healthier emotional responses.
- Parent Training – Educating parents on behavioral management strategies enables them to support their child’s progress effectively.
- Social Skills Training – This focuses on improving interpersonal skills, helping children interact appropriately with peers and adults.
- Exposure Therapy – Gradually introducing children to feared situations facilitates the reduction of anxiety through controlled experiences.
Behavioral therapy is suitable for various age groups, with interventions tailored to meet individual needs. By equipping children with essential skills and strategies, families can navigate behavior challenges while fostering developmental growth.
Key Principles of Behavioral Therapy

Behavioral therapy relies on specific principles to effectively address children’s emotional and behavioral challenges. Central to this approach are reinforcement techniques and behavior modification strategies.
Reinforcement Techniques
Reinforcement techniques enhance desirable behaviors through positive or negative reinforcement.
- Positive Reinforcement: Providing rewards, such as praise or tangible items, encourages a child to repeat a desired behavior. For instance, a child who completes homework on time might receive extra playtime or a small reward.
- Negative Reinforcement: Removing an unpleasant stimulus strengthens desired behavior. For example, a child who cleans their room may avoid losing privileges, reinforcing the cleaning behavior.
- Consistency: Consistent application of reinforcement makes it easier for children to understand expected behaviors. Children recognize patterns and predict outcomes, fostering learning.
Behavior Modification
Behavior modification focuses on altering maladaptive behaviors through structured interventions.
- Functional Behavior Assessment: This assessment identifies specific behaviors, their triggers, and consequences affecting the child. Understanding these factors guides effective intervention strategies.
- Target Behavior Selection: Selecting one or two behaviors for focused intervention prevents overwhelming children. It allows for concentrated efforts on manageable goals, making progress more attainable.
- Intervention Strategies: Techniques such as shaping involve gradually reinforcing closer approximations to the desired behavior. For example, a child learning to share might first receive praise for playing alongside others before being rewarded for sharing toys.
- Monitoring Progress: Regularly tracking progress ensures strategies remain effective. Adjustments based on performance keep interventions aligned with the child’s needs.
- Parent and Caregiver Involvement: Engaging parents and caregivers in the behavior modification process fosters consistency across environments. Training equips them with tools to support positive behavior at home.
Utilizing these key principles enhances the effectiveness of behavioral therapy, helping children navigate their emotional and behavioral challenges while promoting overall development.
Types of Behavioral Therapy for Children
Several effective types of behavioral therapy target children’s specific emotional and behavioral issues. The following therapies focus on structured methods aimed at facilitating positive change.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps children identify and modify negative thoughts and behaviors. It emphasizes the link between thoughts, feelings, and actions, making it suitable for conditions like anxiety and depression. In CBT, children learn to challenge unproductive thoughts and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Sessions often include structured exercises, role-playing, and journaling to reinforce positive behaviors and thoughts. Research indicates that CBT significantly reduces symptoms and improves emotional regulation in children.
Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT)
Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT) fosters a positive parent-child relationship while addressing disruptive behaviors. PCIT focuses on improving interactions through training sessions structured for both parents and children. Parents learn effective discipline techniques and ways to reinforce desirable behaviors, which helps decrease negative behavior patterns. The therapy involves live coaching, where therapists guide parents in real-time during play sessions with their children. Studies show that PCIT significantly enhances behavioral outcomes and strengthens family dynamics.
Effectiveness of Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy demonstrates significant effectiveness in addressing various emotional and behavioral challenges in children. Research findings and case studies showcase its impact on enhancing children’s mental health and social functioning.
Research Findings
Research highlights behavioral therapy’s efficacy through various studies. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry revealed that Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) reduces anxiety symptoms in children by approximately 60%. Another study in Behavior Research and Therapy confirmed that Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT) significantly decreases disruptive behaviors, with up to 75% of participants reporting improved parent-child relationships. Furthermore, longitudinal studies indicate that early behavioral therapy interventions lead to lasting behavioral improvements, suggesting that timely support enhances long-term outcomes.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies illustrate the tangible benefits of behavioral therapy. One case involved a nine-year-old girl diagnosed with ADHD. After undergoing CBT, her parents reported a noticeable reduction in impulsivity and improved concentration at school within three months. Another case centered on a boy with social skills deficits. Through PCIT, he developed effective communication strategies and displayed increased confidence in social settings, leading to more meaningful friendships. These examples underscore how tailored behavioral interventions positively influence children’s emotional and behavioral landscapes, supporting their overall development.
Challenges in Implementing Behavioral Therapy
Implementing behavioral therapy for children presents several challenges that can affect its success.
- Resistance to Change: Children may resist engaging in therapy due to discomfort with sharing emotions or altering familiar behaviors. Ensuring a trusting relationship between the therapist and child can mitigate this issue.
- Parental Involvement: Engaging parents in the therapeutic process remains crucial. Parents must consistently apply behavior modification techniques at home. Without their participation, therapeutic gains can diminish.
- Consistency of Application: Maintaining consistent implementation of behavioral strategies across settings—home, school, and therapy—proves essential. Inconsistencies can confuse children, hindering progress and understanding.
- Individual Differences: Each child’s unique needs and responses to therapy complicate a one-size-fits-all approach. Tailoring interventions based on the child’s personality, developmental stage, and specific challenges increases effectiveness.
- Skill Transfer: Children may struggle to apply learned behaviors in real-world situations. Practicing skills in varied contexts helps reinforce behavior changes and enhances confidence.
- Resource Availability: Access to trained therapists and appropriate resources can limit the implementation of effective behavioral therapy. Under-resourced communities may struggle to provide adequate support.
- Time Commitment: Families may face challenges in committing time for therapy sessions and home practice. Balancing therapy with school and other obligations often becomes difficult.
Navigating these challenges requires collaboration among therapists, parents, and schools to ensure behavioral therapy effectively addresses children’s emotional and behavioral issues.
Behavioral therapy stands as a powerful tool for addressing the emotional and behavioral challenges faced by children. By focusing on structured interventions and reinforcement techniques, it helps children develop essential coping strategies and fosters positive behavioral changes. The involvement of parents and caregivers enhances the therapy’s effectiveness, creating a supportive environment for growth.
As families navigate the complexities of behavioral therapy, understanding its principles and methods can empower them to make informed decisions. With the right approach and commitment, behavioral therapy can lead to significant improvements in children’s mental health and social skills, paving the way for healthier relationships and a brighter future.